Stimulants: What They Are, How They Work, and What You Need to Know
When you think of stimulants, substances that increase alertness, energy, and attention by boosting activity in the central nervous system. Also known as nervous system activators, they’re used medically for conditions like ADHD and narcolepsy—but also misused for performance or mood enhancement. Not all stimulants are created equal. Some are prescription-only, like methylphenidate or amphetamines. Others, like caffeine or nicotine, are legal and widely consumed. But whether it’s a pill, a cup of coffee, or a nicotine patch, stimulants change how your brain and body respond to fatigue, stress, and focus.
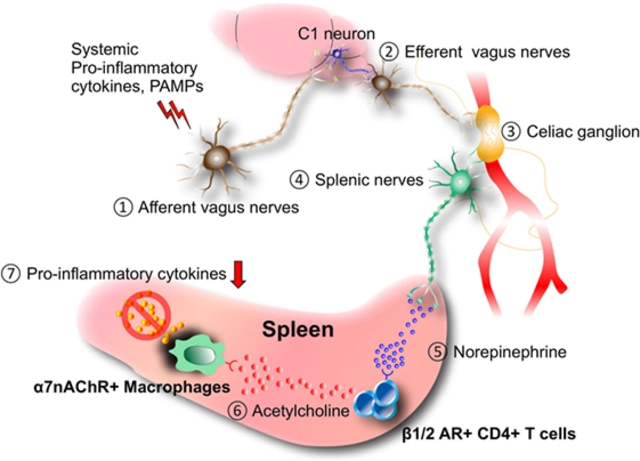
What happens when you take a stimulant? Your brain releases more dopamine and norepinephrine. That’s why you feel awake, sharp, or even euphoric. But that same surge can lead to jitters, a racing heart, or trouble sleeping. Long-term use—even as prescribed—can cause tolerance, meaning you need more to get the same effect. Some people develop dependence, where stopping feels worse than never using it. And in high doses or with misuse, stimulants can trigger anxiety, paranoia, or even heart problems. The stimulant side effects, ranging from mild insomnia to serious cardiovascular strain are real, and they’re not always obvious until it’s too late.
There’s also the issue of stimulant dependence, a pattern of compulsive use despite negative consequences. It’s not just about addiction. It’s about losing control over when, how much, and why you’re using. People often start with a prescription, then tweak the dose. Others grab caffeine pills to study longer or stimulants to stay up for work. What starts as a tool can become a crutch. And when the effect fades, the crash hits hard—fatigue, irritability, brain fog. That cycle keeps people trapped.
What’s missing from most conversations is what comes after. If you’re trying to cut back, what replaces the energy? Sleep hygiene, structured routines, and non-stimulant focus aids like behavioral strategies or certain supplements can help. Some people switch to low-dose prescription options with fewer risks. Others find that addressing the root cause—like poor sleep or untreated anxiety—makes stimulants unnecessary. The goal isn’t always to quit cold turkey. It’s to understand why you reached for them in the first place.
Below, you’ll find real-world guides on managing stimulant-related issues—from handling side effects to understanding how they interact with other meds. You’ll see how people safely adjust doses, recognize warning signs, and find alternatives that actually work. No fluff. No hype. Just clear, practical info based on what patients and doctors have learned the hard way.
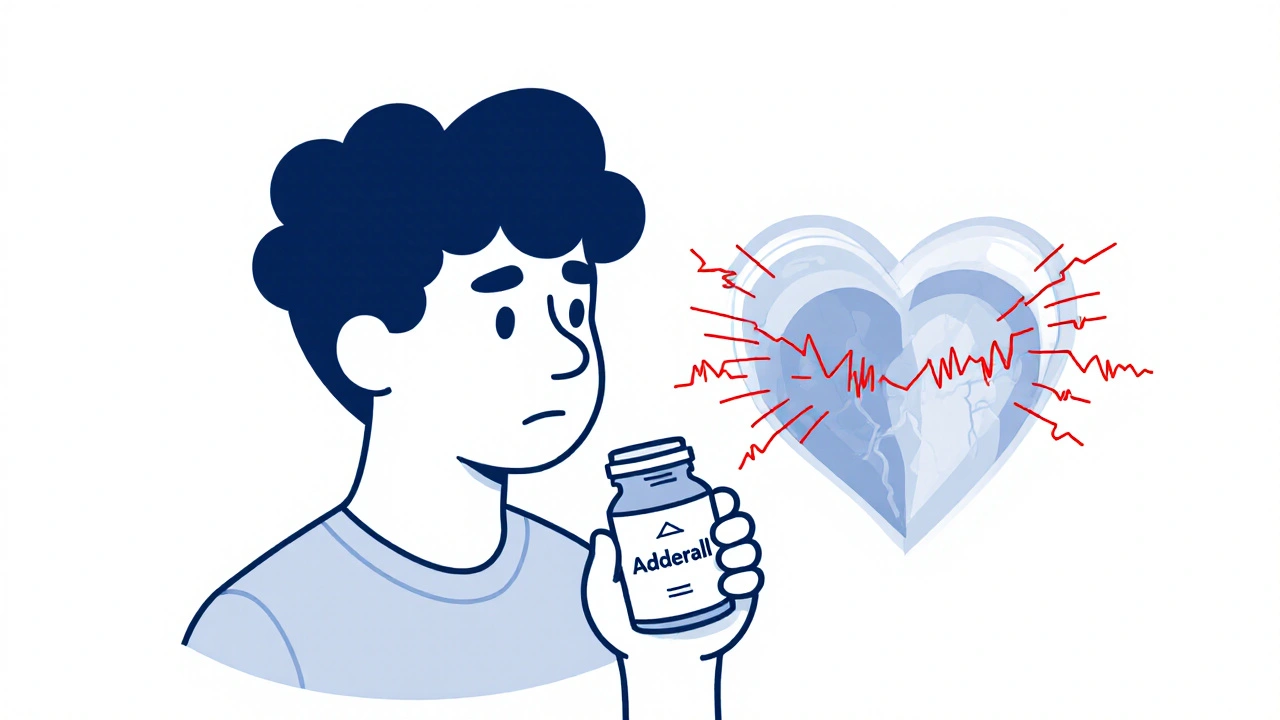
Stimulants for ADHD can improve focus but carry a small risk of cardiac arrhythmias. Learn who’s at risk, how to assess heart health, and what non-stimulant alternatives actually work.