Calcium Channel Blockers: What They Are, How They Work, and Which Ones Work Best
When your heart and blood vessels need to relax, calcium channel blockers, a class of medications that stop calcium from entering heart and blood vessel cells, reducing pressure and improving blood flow. Also known as calcium antagonists, they’re one of the most common ways doctors treat high blood pressure and chest pain. Unlike diuretics or beta-blockers, they don’t flush out fluid or slow your heart rate directly—they simply take the strain off your arteries so your heart doesn’t have to work as hard.
Not all calcium channel blockers are the same. nifedipine, a short-acting drug often used in Adalat, opens up arteries quickly and is good for sudden spikes in blood pressure. Then there’s amlodipine, a longer-acting option that stays in your system for days, making it a daily staple for steady control. If your heart is racing or you have angina, your doctor might pick diltiazem or verapamil, which also slow down your heart’s electrical signals, not just widen your vessels. Each has its own rhythm, side effects, and best-use cases.
People often switch between these drugs when side effects like swelling in the ankles, dizziness, or constipation become a problem. Some respond better to amlodipine’s steady effect, while others need nifedipine’s quick action during flare-ups. And if you’re on other meds—like statins or grapefruit juice—you need to know how they interact. That’s why understanding the difference isn’t just academic; it’s personal. The right choice can mean fewer trips to the ER, better sleep, and less daily discomfort.
What you’ll find below are real comparisons and practical guides—how Adalat stacks up against amlodipine, why some people tolerate one drug but not another, and what to watch for when your doctor suggests a switch. No fluff. No marketing. Just what works, what doesn’t, and why it matters for your health.
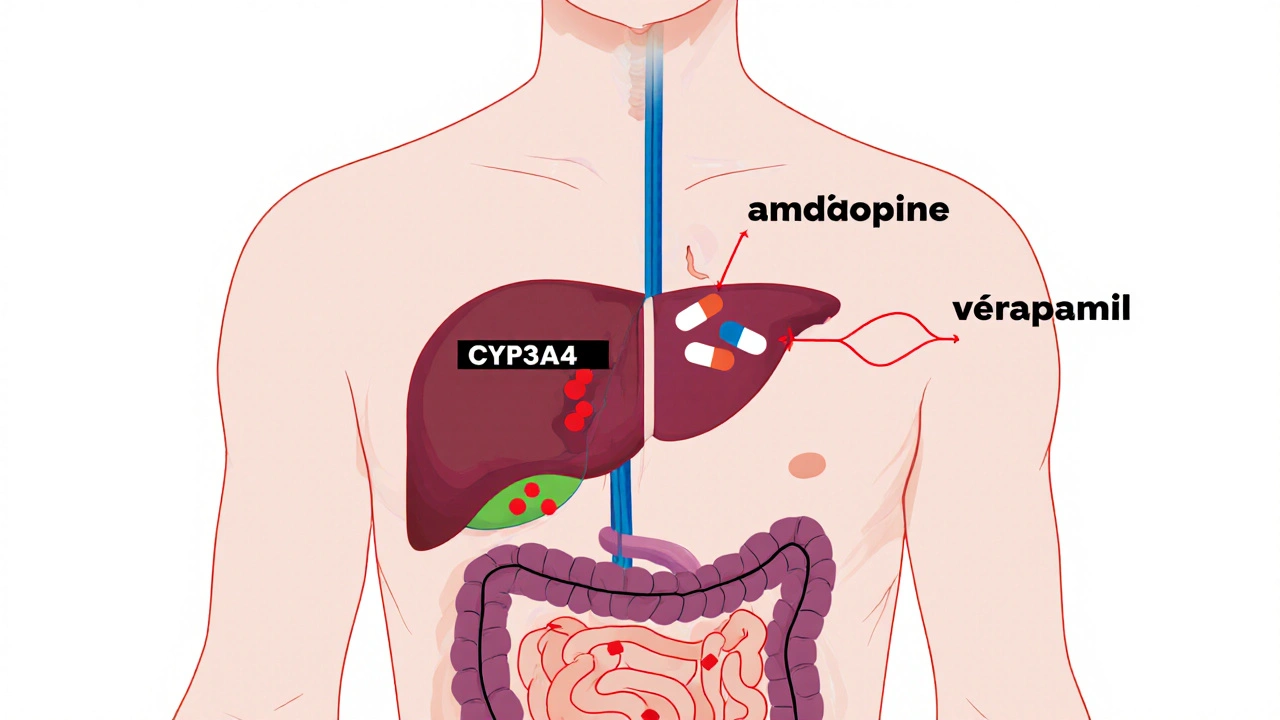
Calcium channel blockers are widely used for high blood pressure and heart conditions, but their safety depends heavily on how your body metabolizes them. Learn which ones are safest, which drugs and foods to avoid, and how to prevent dangerous interactions.





