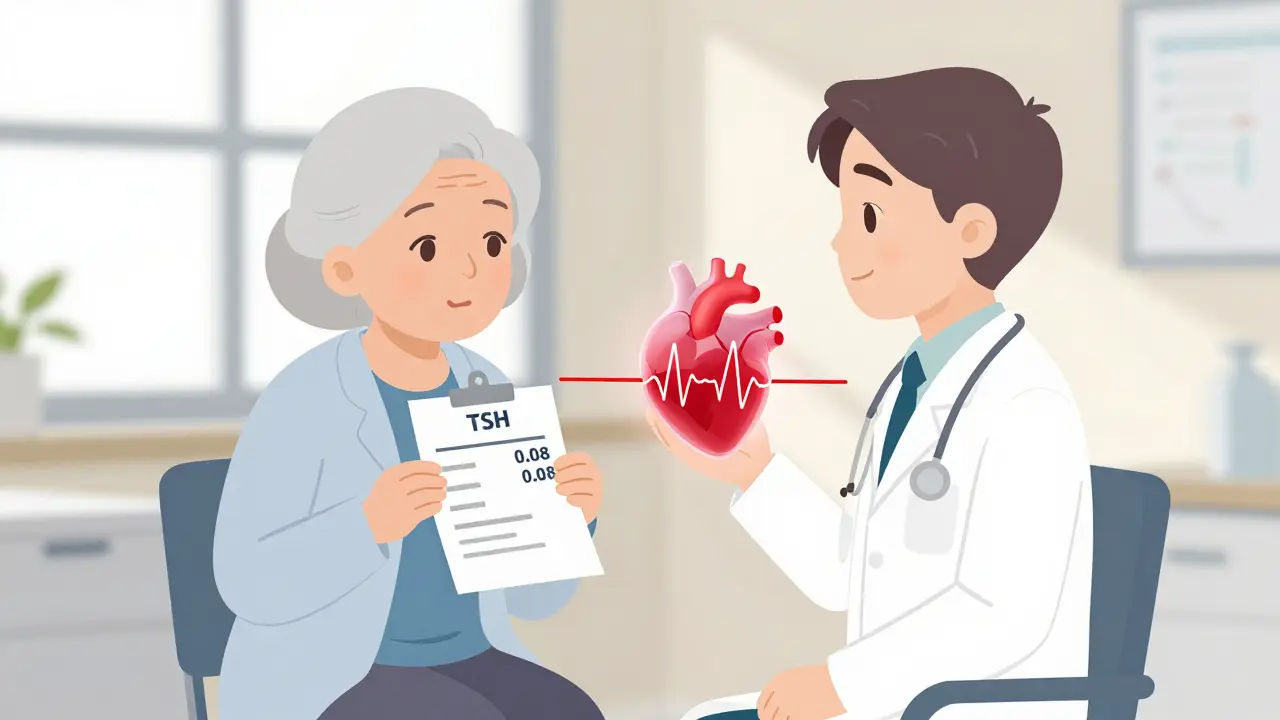
Subclinical Hyperthyroidism: Heart Risks and When to Treat
Subclinical hyperthyroidism may not cause symptoms, but it raises heart risks-especially in older adults. Learn when low TSH levels require treatment and how to protect your heart and bones.
When we talk about heart risks, factors that increase your chance of heart attack, stroke, or other cardiovascular events. Also known as cardiovascular risk, it's not just about high blood pressure or bad cholesterol—it's often about what you're taking, what your genes say, and how those two things interact. Many people think if their cholesterol numbers look fine, they're safe. But that’s not always true. Lipoprotein(a), a genetic form of cholesterol that acts like a silent timer for heart disease can double your risk—even if your LDL is perfect. It doesn’t show up on standard tests, and most doctors don’t check for it unless you’ve had early heart trouble or have a family history.
Then there’s the meds. Statin side effects, like muscle pain or fatigue make people quit life-saving drugs. But here’s the thing: most of those people could stay on statins with a simple dose tweak or by switching to another one. It’s not about giving up—it’s about finding the right fit. And it’s not just statins. Drug interactions, how one medication changes how another works in your body can quietly boost heart risks. A common allergy pill, a sleep aid, even an OTC painkiller—some mix in ways that raise blood pressure, mess with heart rhythm, or strain your liver. These aren’t rare cases. They happen every day, often without anyone noticing.
What you’re not seeing on your lab report might be the real threat. That’s why understanding your personal mix—genes, meds, lifestyle—is more important than any single number. You don’t need to be a scientist to protect your heart. You just need to know what questions to ask, what tests to push for, and which meds might be working against you instead of for you. Below, you’ll find clear, no-fluff guides on how to spot hidden dangers, manage side effects without quitting treatment, and understand the real science behind what’s putting your heart at risk.

Subclinical hyperthyroidism may not cause symptoms, but it raises heart risks-especially in older adults. Learn when low TSH levels require treatment and how to protect your heart and bones.
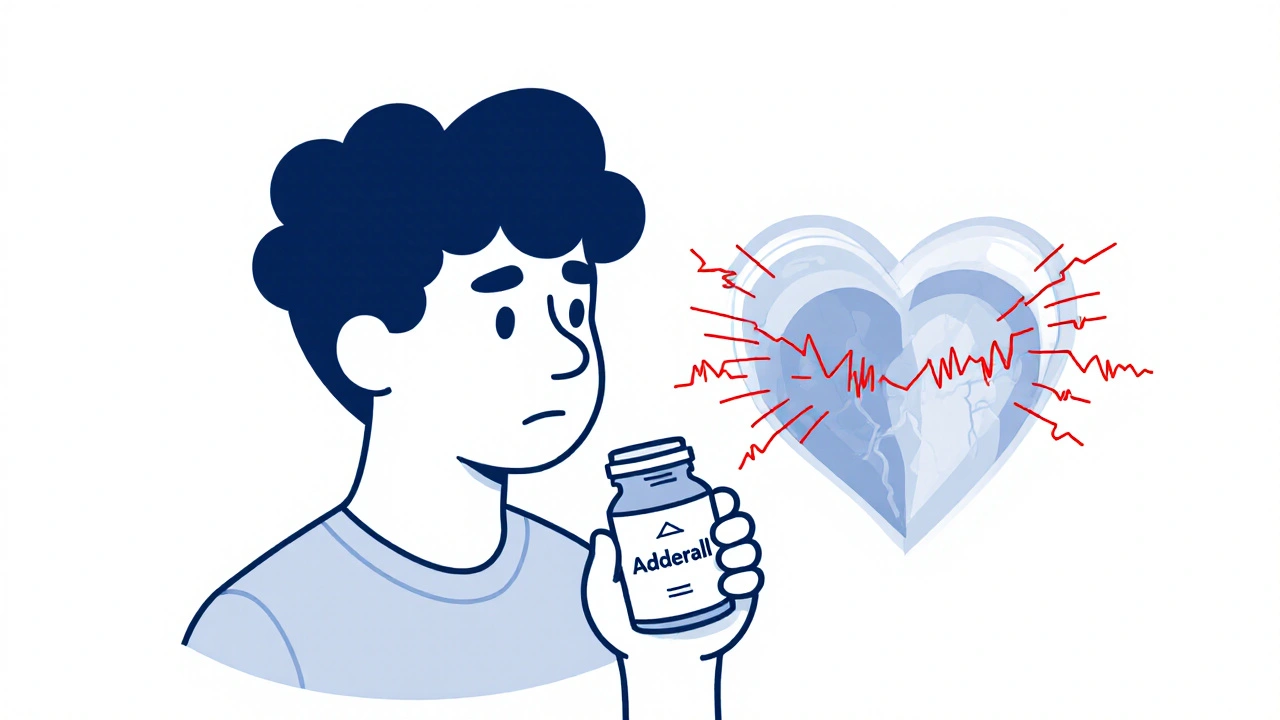
Stimulants for ADHD can improve focus but carry a small risk of cardiac arrhythmias. Learn who’s at risk, how to assess heart health, and what non-stimulant alternatives actually work.