SSRI Drug Interactions: What You Need to Know to Stay Safe
When you take an SSRI, a type of antidepressant that increases serotonin in the brain to improve mood. Also known as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, these drugs are among the most prescribed for depression and anxiety—but their safety depends heavily on what else you’re taking. SSRIs like sertraline, fluoxetine, and escitalopram work by blocking serotonin reabsorption, but that same mechanism can turn harmless combinations into serious risks.
The biggest danger? serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening reaction caused by too much serotonin in the nervous system. It doesn’t take much: mixing an SSRI with another serotonin-boosting drug—like tramadol, dextromethorphan, or even St. John’s wort—can trigger it. Symptoms include confusion, rapid heart rate, high blood pressure, muscle rigidity, and fever. You won’t always know it’s happening until it’s advanced, which is why knowing your meds matters more than ever. Another hidden risk comes from CYP450 metabolism, the liver system that breaks down most drugs, including SSRIs. Some SSRIs, like paroxetine and fluoxetine, strongly inhibit CYP2D6, slowing down how other drugs are processed. That means painkillers, blood thinners, or even beta-blockers can build up to toxic levels in your body. Even common OTC meds like cold remedies or sleep aids can become risky when paired with an SSRI.
It’s not just pills. Supplements like 5-HTP or tryptophan, herbal teas like kava, and even certain foods like aged cheeses or cured meats (when paired with MAOIs, which some people take alongside SSRIs) can add fuel to the fire. And it’s not just about what you take—it’s about timing. Stopping an SSRI too quickly or starting a new drug too soon after can leave you vulnerable to withdrawal or interaction effects. That’s why pharmacists now routinely screen for these combos before filling prescriptions. If you’re on an SSRI, don’t assume your doctor knows every supplement you take. Write them down. Bring them to every appointment. Ask: "Could this interact with my antidepressant?" The answer might save your life.
Below, you’ll find real-world guides on how SSRIs interact with opioids, statins, calcium channel blockers, and more—backed by clinical evidence and patient experiences. These aren’t theoretical warnings. They’re the kind of details that keep people out of the ER.
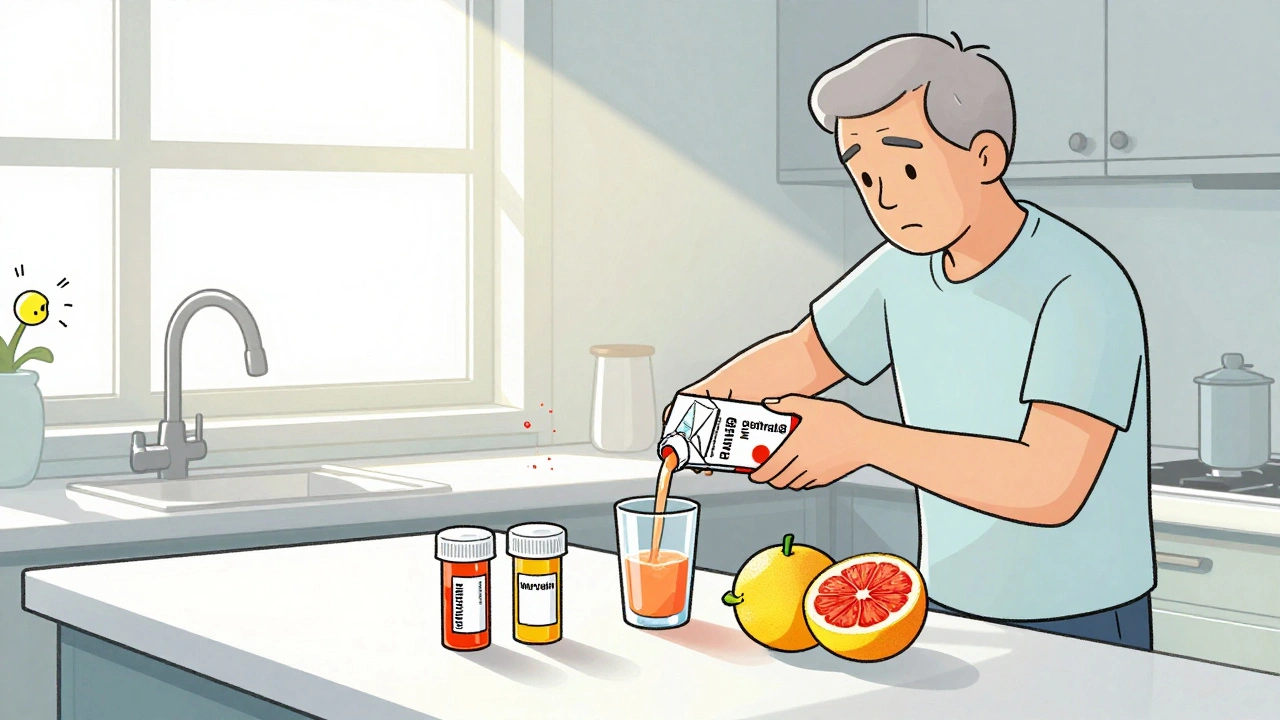

Grapefruit can dangerously increase levels of warfarin and certain SSRIs by blocking CYP450 enzymes. Learn which medications are at risk, why timing doesn't help, and what to do instead.