Author: Iain French - Page 2

Grapefruit juice can dangerously increase drug levels in your blood by blocking a key enzyme. Over 85 medications, including statins and blood pressure drugs, interact with it. Even small amounts can cause serious harm. Avoid it completely if you're on affected meds.
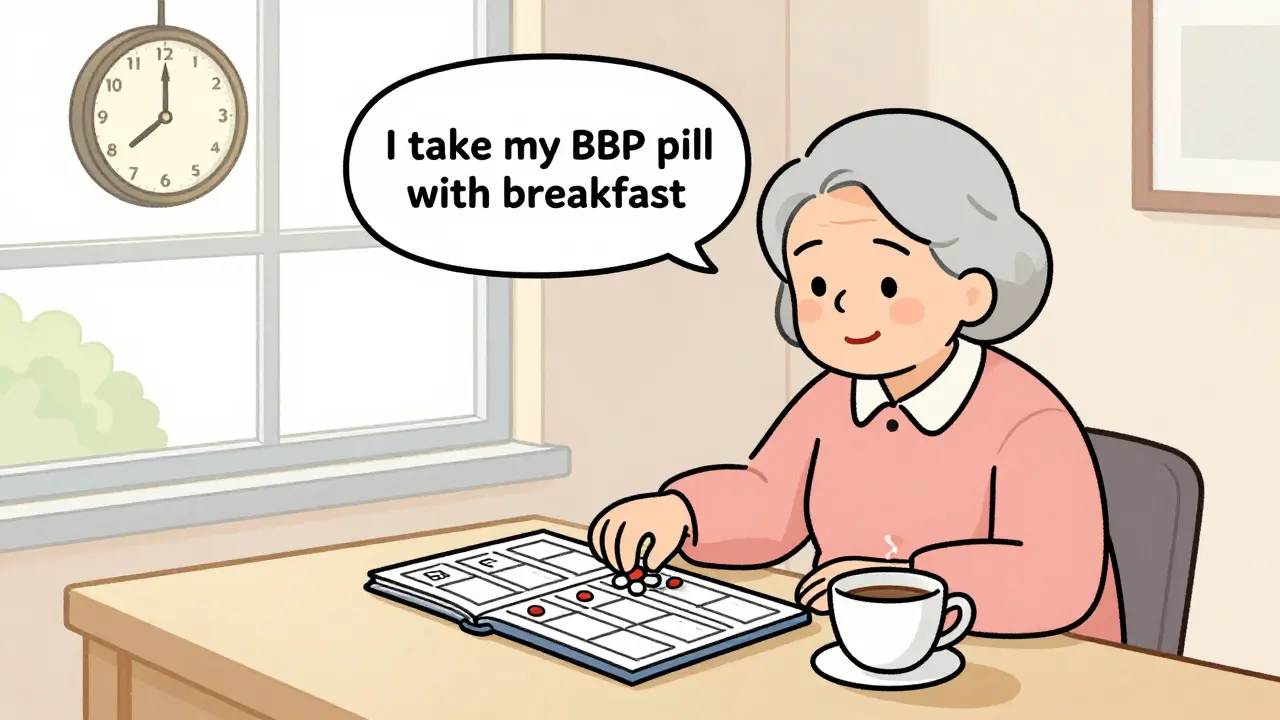
Skipping prescription doses can lead to serious health risks, from drug resistance to life-threatening complications. Learn why timing matters, which medications are most sensitive, and how to stay on track every day.
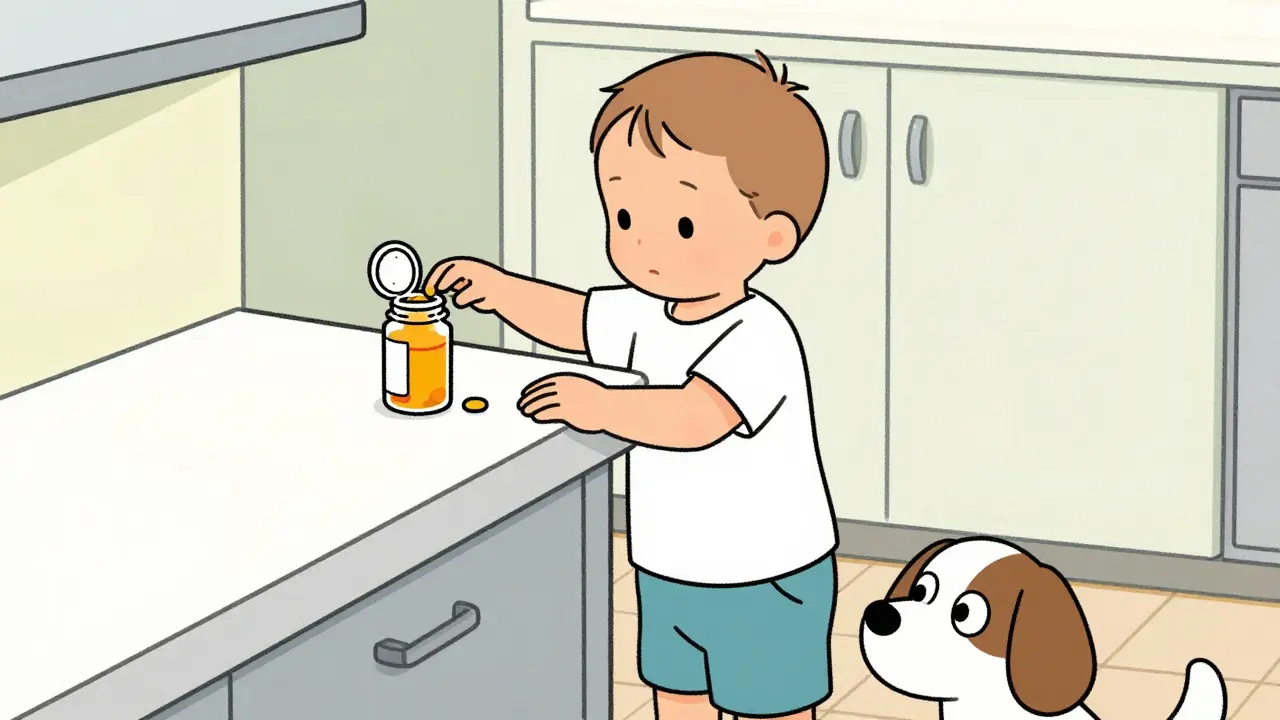

Accidental medication ingestion harms tens of thousands of children and pets each year. Learn how locked storage, separate locations for human and pet meds, and proper labeling can prevent poisonings and save lives.

Learn how to find the cheapest generic medications online using comparison shopping engines. Save up to 80% on prescriptions by comparing verified pharmacies and avoiding scams.
Diabetic neuropathy causes painful nerve damage, but with tight blood sugar control, safe medications, and lifestyle changes, you can reduce pain and protect your nerves. Learn what works-and what doesn’t.

The Military Shelf Life Extension Program proves many expired drugs remain stable and effective for years beyond their labeled dates - saving billions and challenging outdated pharmaceutical norms.

Agranulocytosis from medications can be deadly, but it's preventable with proper blood monitoring. Learn which drugs carry the highest risk, how to spot early signs of infection, and why regular blood tests save lives.
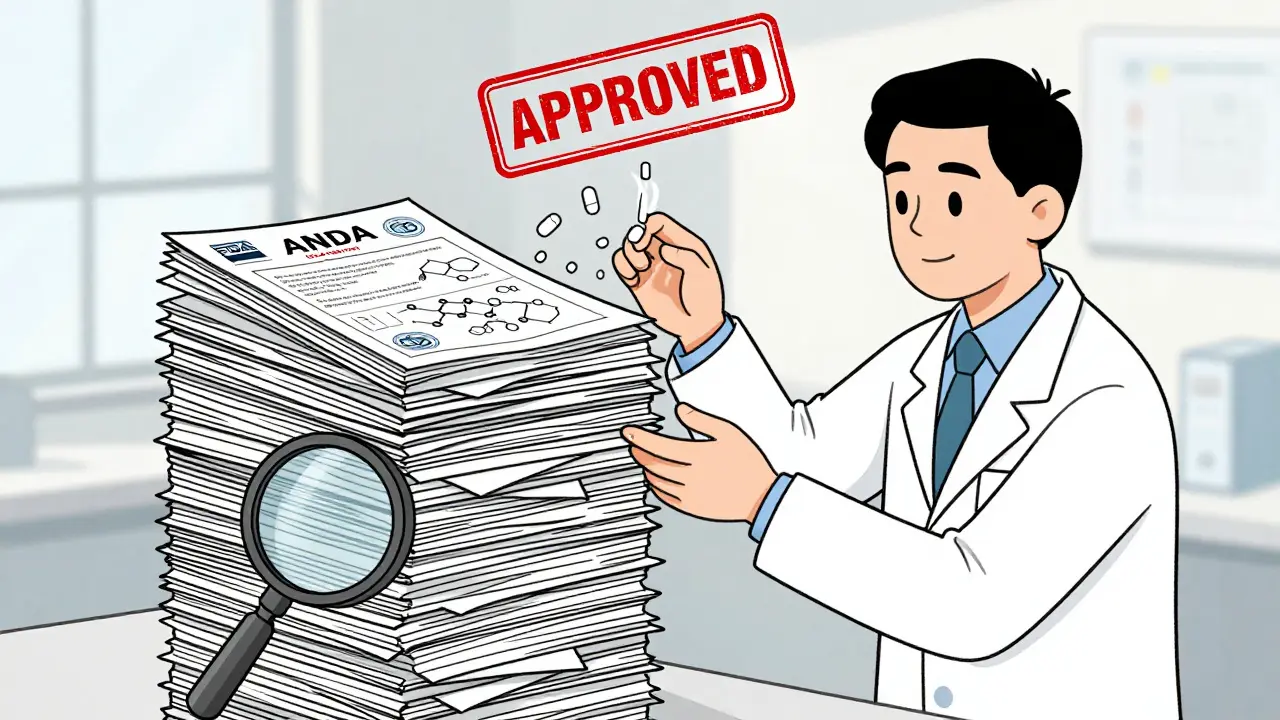
Discover how generic drugs go from FDA approval via ANDA to your pharmacy shelf - the science, regulation, and business steps that make affordable medication possible.
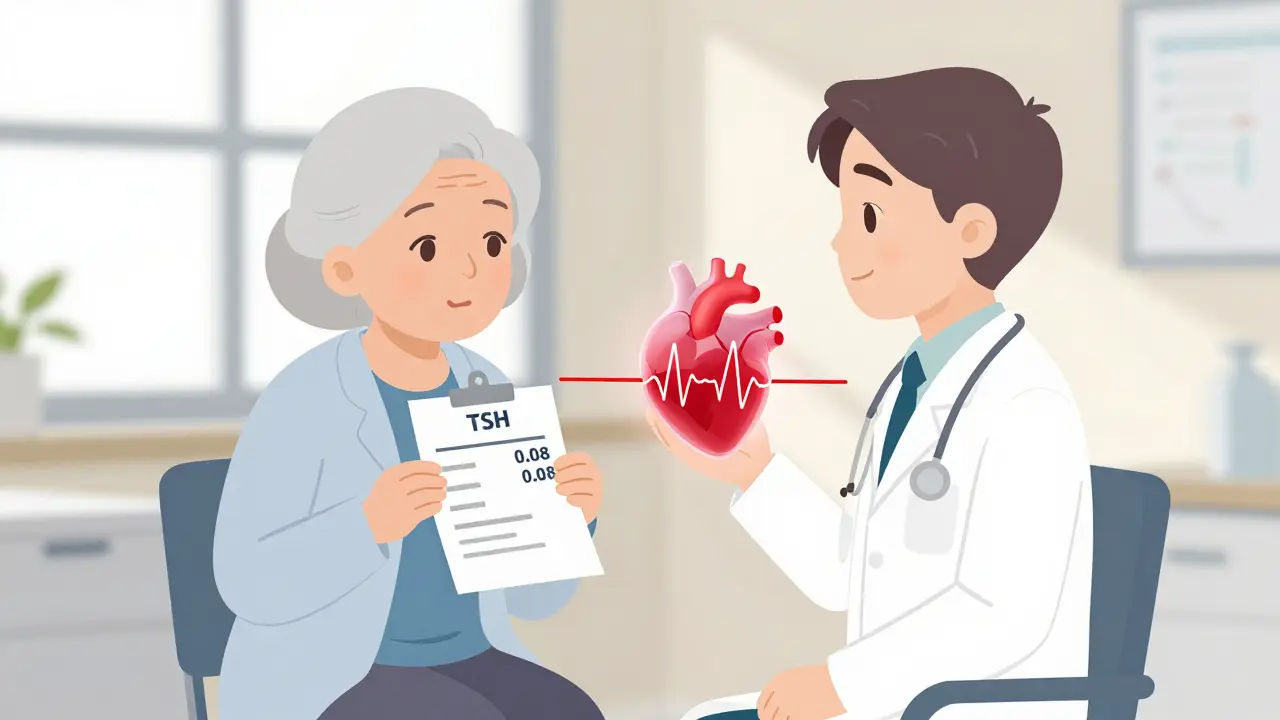
Subclinical hyperthyroidism may not cause symptoms, but it raises heart risks-especially in older adults. Learn when low TSH levels require treatment and how to protect your heart and bones.
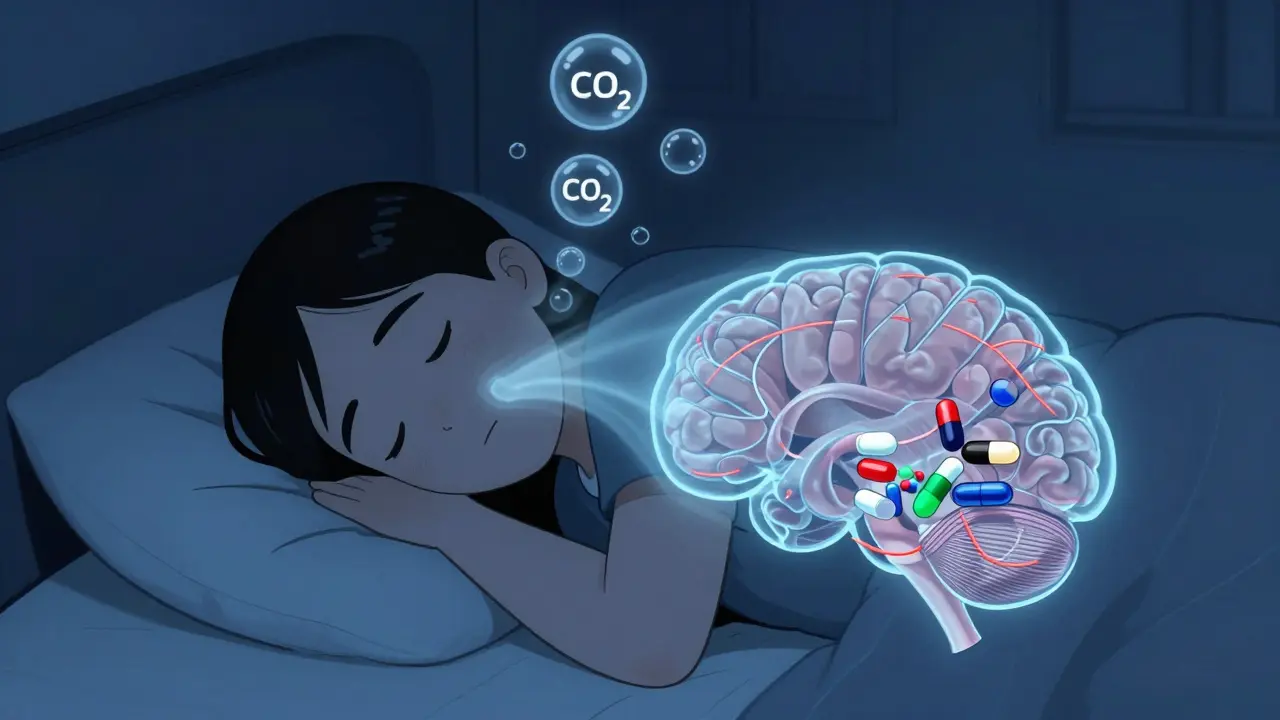
Opioids can cause dangerous breathing pauses during sleep, even in people without prior sleep apnea. This hidden risk leads to overdose deaths at night. Learn how opioids disrupt breathing, who’s most at risk, and what to do to stay safe.