Author: Iain French - Page 3
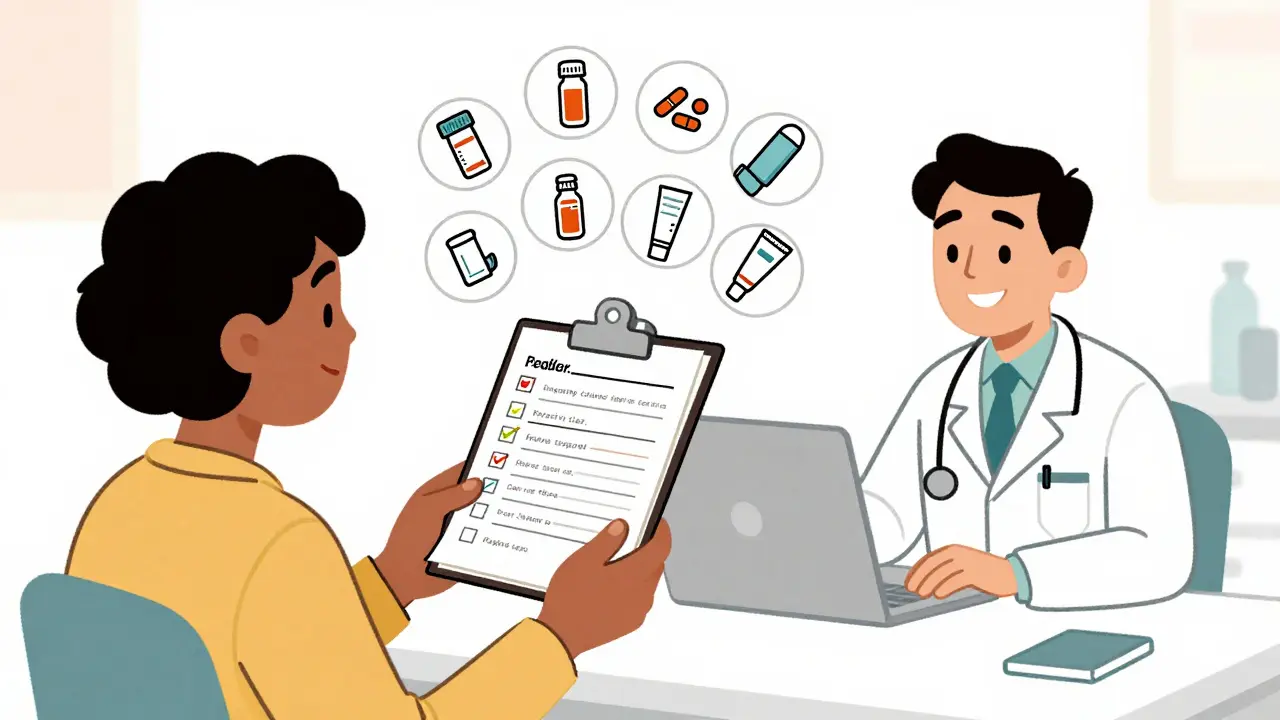

A complete, up-to-date medication list prevents dangerous errors, improves communication between doctors, and keeps you safe during hospital visits or care transitions. Learn what to include and how to keep it accurate.
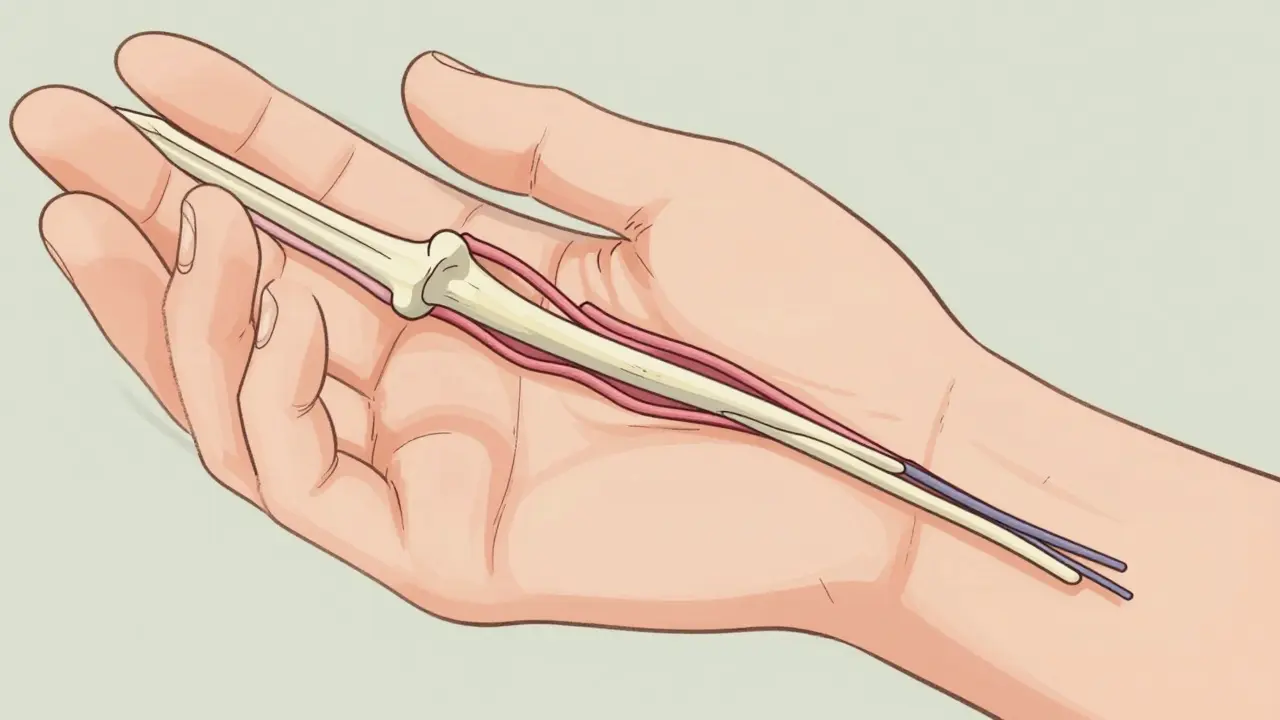
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common nerve compression disorder causing numbness, pain, and weakness in the hand. Learn the signs, stages, and proven treatments-from splints to surgery-before permanent damage occurs.
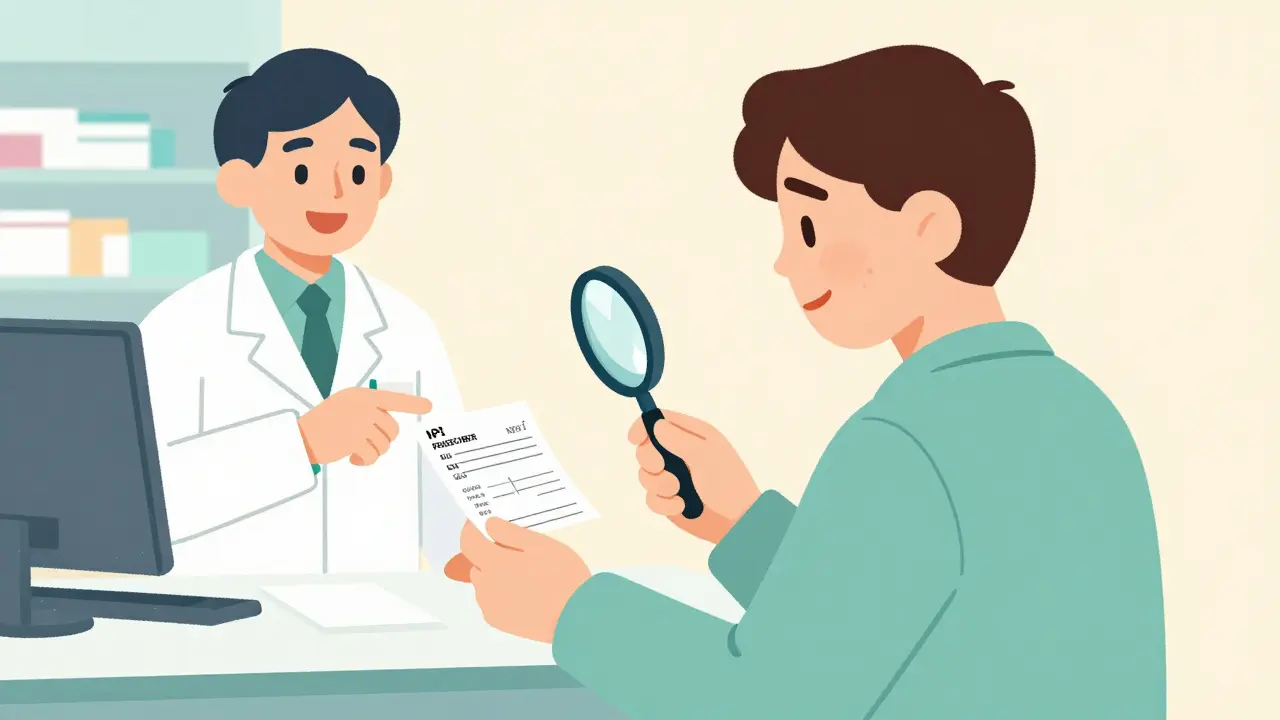

Verifying prescriber and pharmacy details on your medication label prevents dangerous errors. Learn what to check, when to check it, and how to catch mistakes before they harm you.

Pharmacodynamic drug interactions occur when drugs alter each other's effects at the target site, not by changing levels in the body. These can be deadly-like SSRIs with MAOIs-or lifesaving, like antibiotic combos. Know the risks.
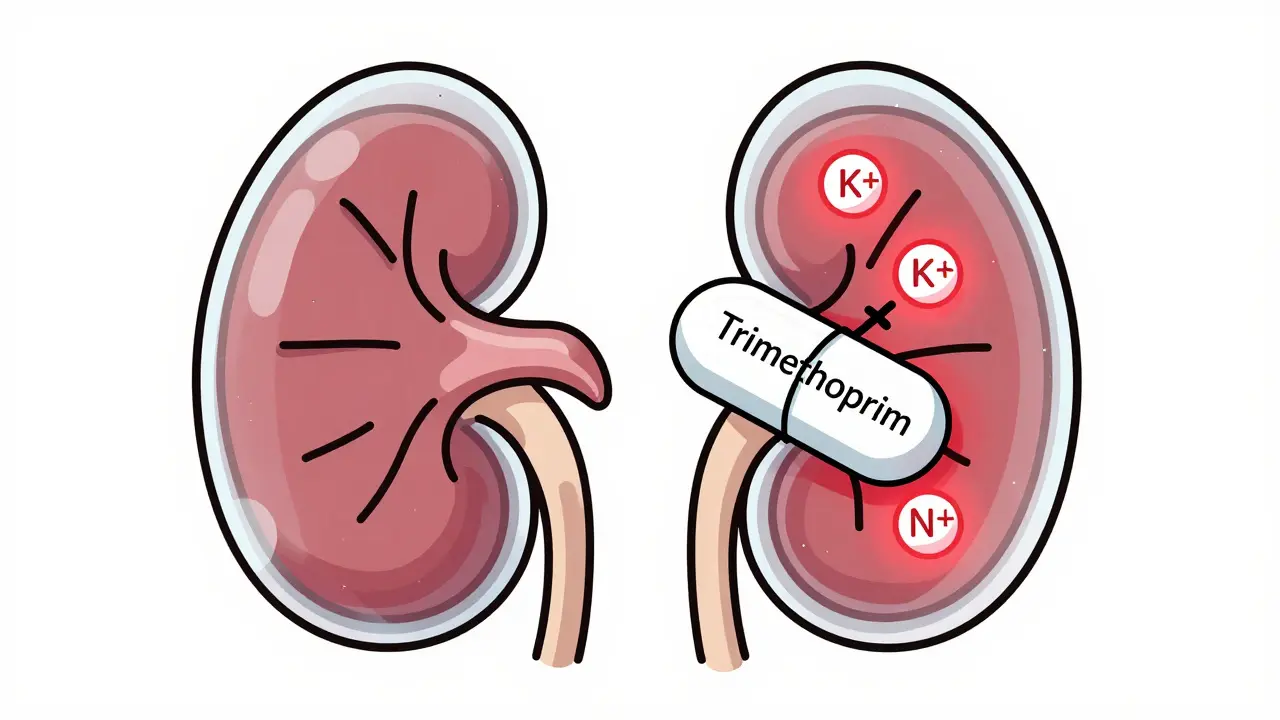
Trimethoprim, found in Bactrim and Septra, can cause dangerous spikes in potassium levels-even in people with healthy kidneys. Learn who’s at risk, how it happens, and what to ask your doctor before taking it.
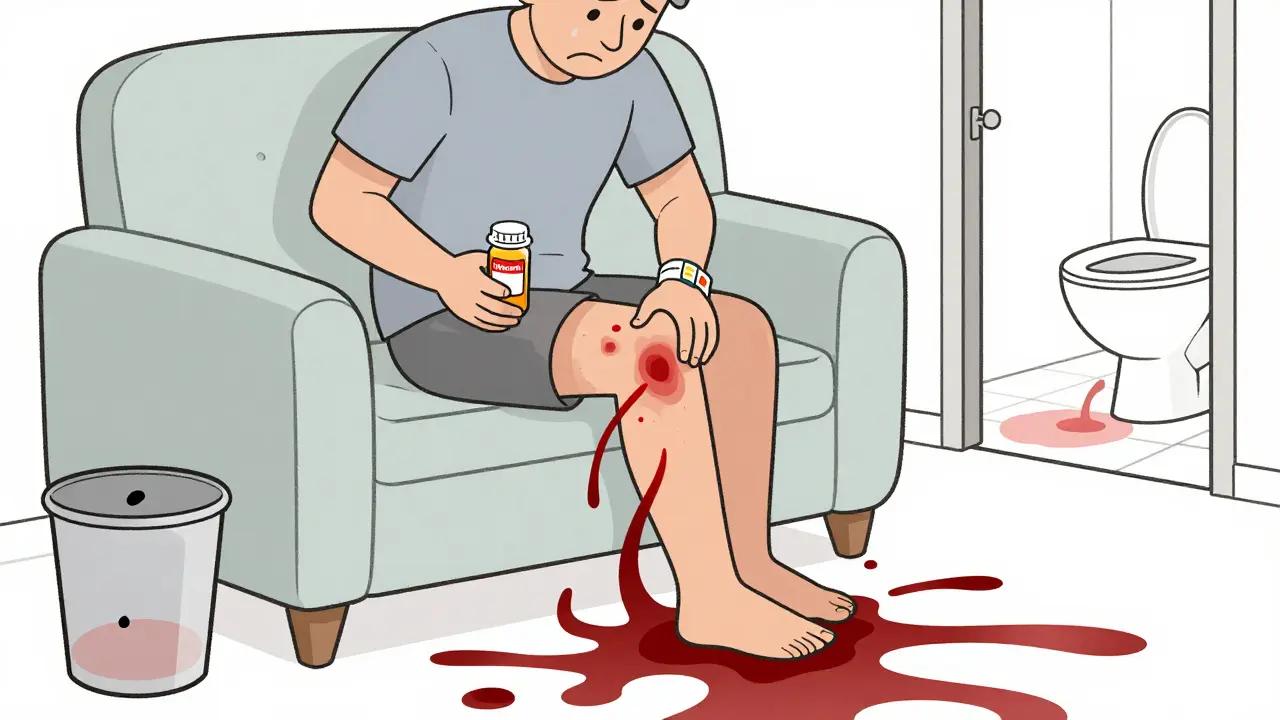

A blood thinner overdose can cause life-threatening internal bleeding with subtle symptoms. Know the warning signs, act fast, and follow emergency steps to survive. Prevention and quick response save lives.

Despite being equally safe and effective, generic drugs face widespread mistrust fueled by misleading media coverage. Learn how news stories shape public perception-and what you can do to make informed choices.

Pharmaceutical advertising in the U.S. heavily promotes branded drugs, shaping patient beliefs that generics are inferior - even though they’re chemically identical. This marketing distorts treatment choices and drives up costs.
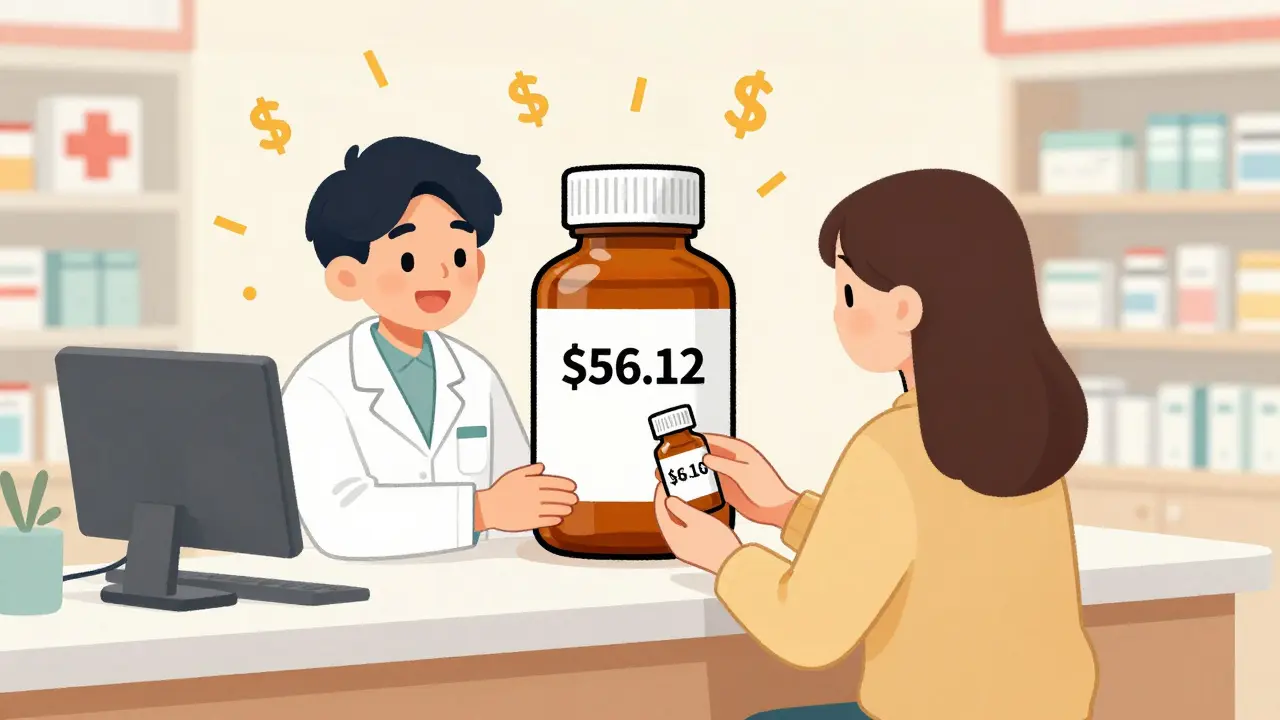

Generic medications save the U.S. healthcare system over $400 billion a year, making up 90% of prescriptions but only 1.5% of drug spending. Learn how generics work, why they're safe, and how to save hundreds annually by choosing them.
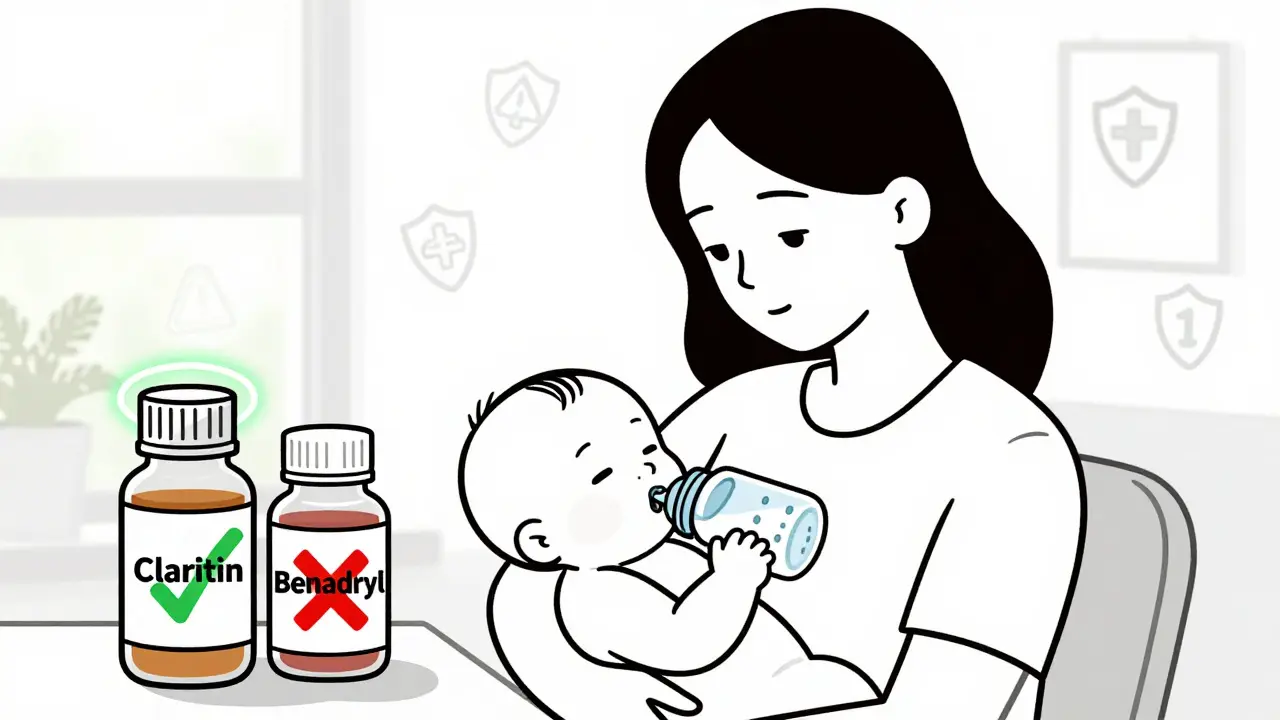

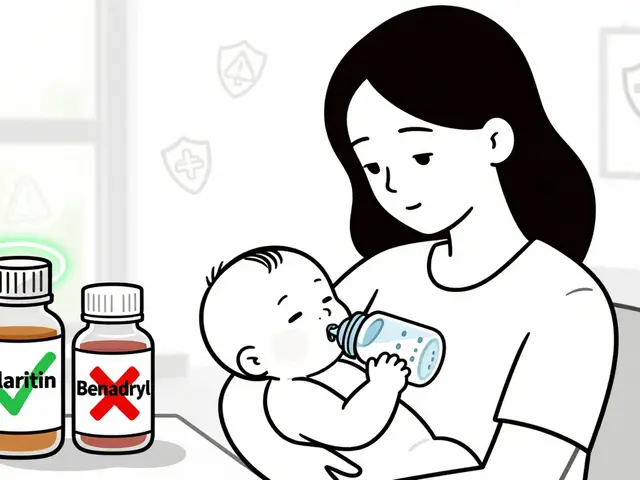
Learn which antihistamines and pain relievers are safe to take while breastfeeding, which ones to avoid, and how to protect your baby’s health without sacrificing your own comfort.